Category: Soil
-

Redox Potential
Read More: Redox PotentialRedox potential (Eh) and pH are two important factors that play significant roles in soil/plant/microorganism systems. They act as drivers, influencing various processes and interactions within these systems. This transdisciplinary overview aims to provide an integrated understanding of the relationships between redox potential, pH, and the functioning of soil/plant/microorganism systems. Thus, highlighting potential opportunities for…
-
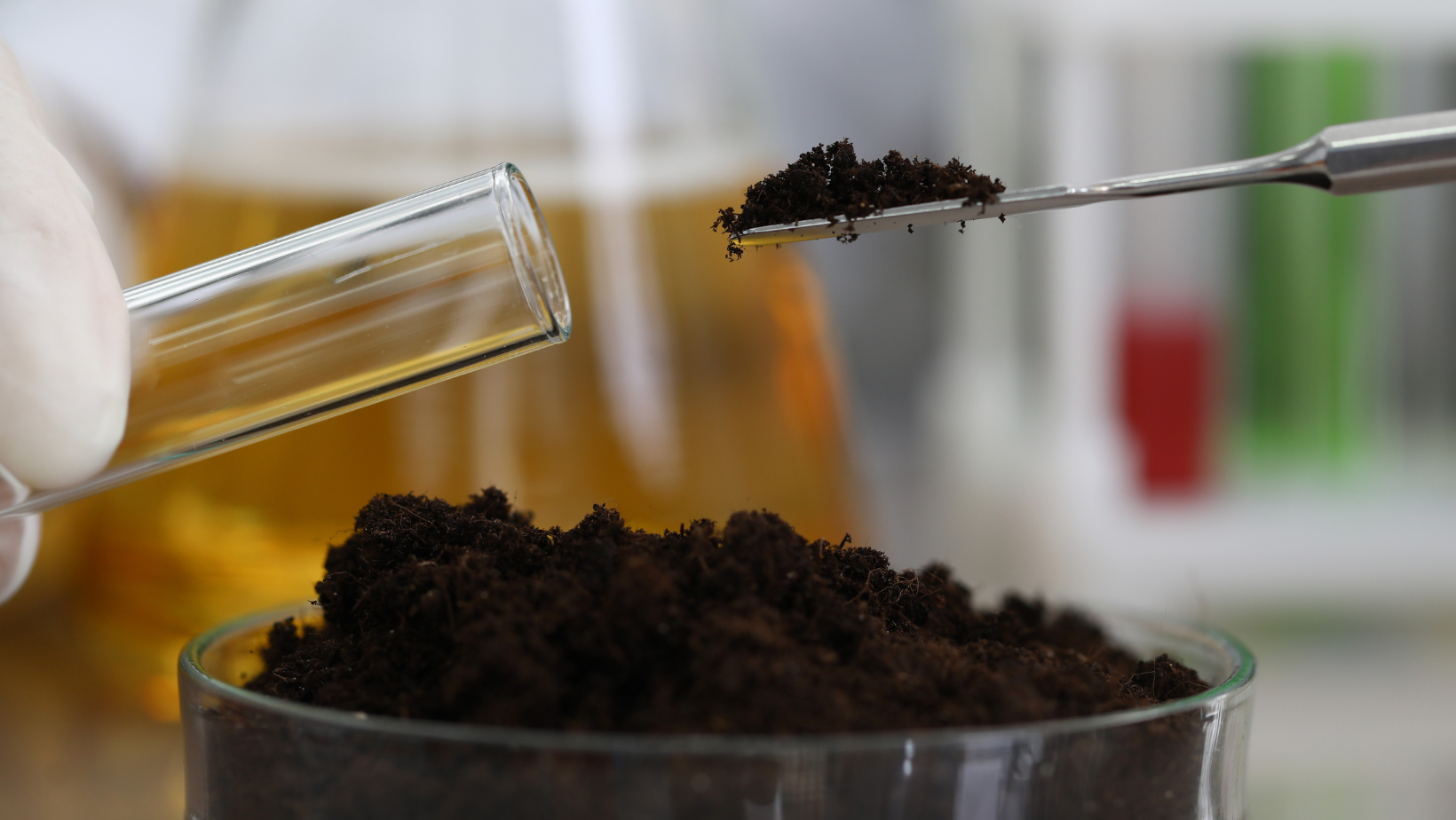

Metagenomic Soil Testing
Read More: Metagenomic Soil TestingMetagenomic soil testing is a powerful tool that provides several benefits for understanding and analyzing soil microbiomes. Greensmiths, Inc. and our distributors, use this detailed testing to formulate custom blends of fertilizer. Blends are created based on each customers’ specific needs and soil requirements. Some key benefits of metagenomic soil testing include: Comprehensive analysis: Metagenomic…
-
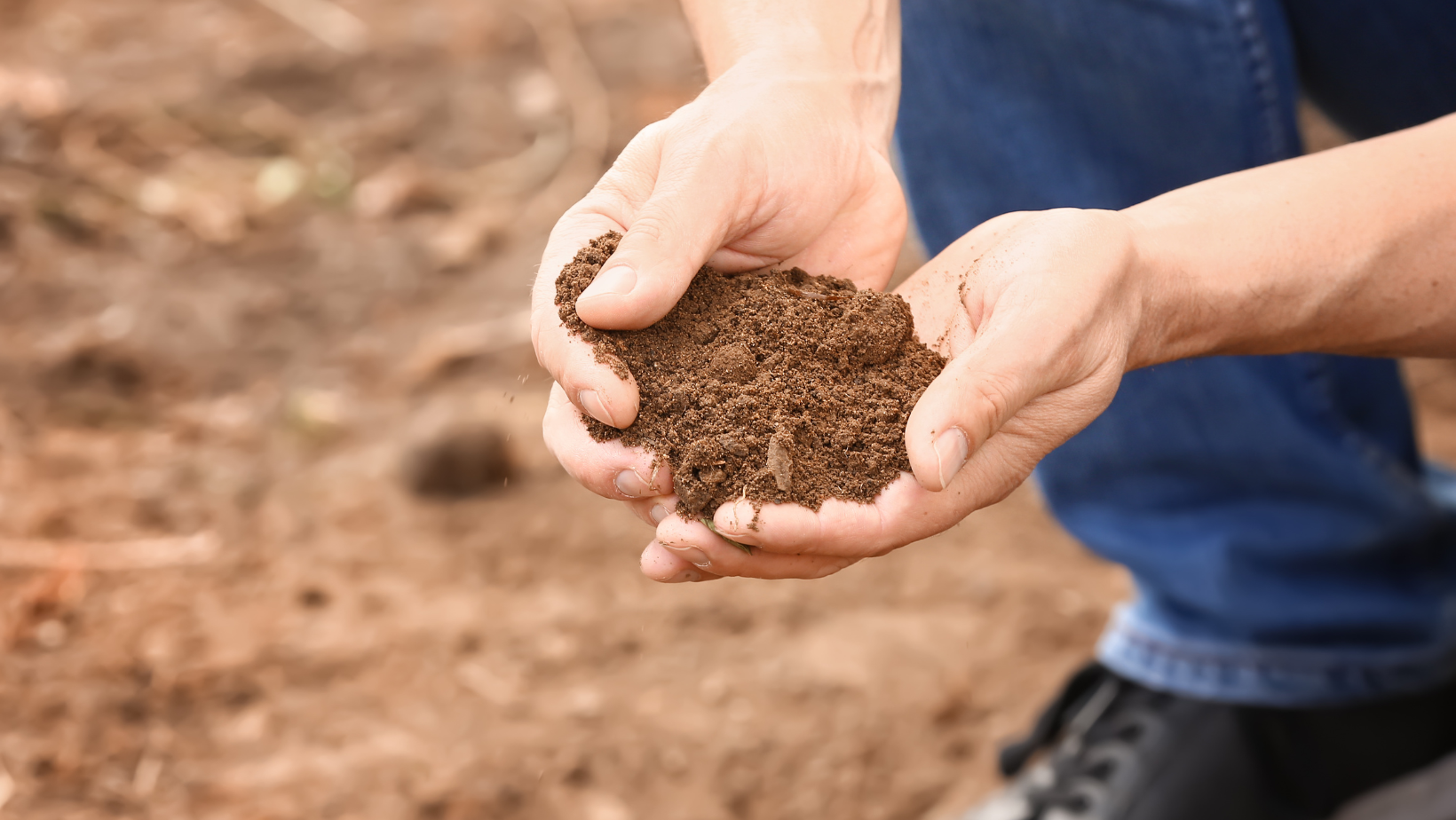

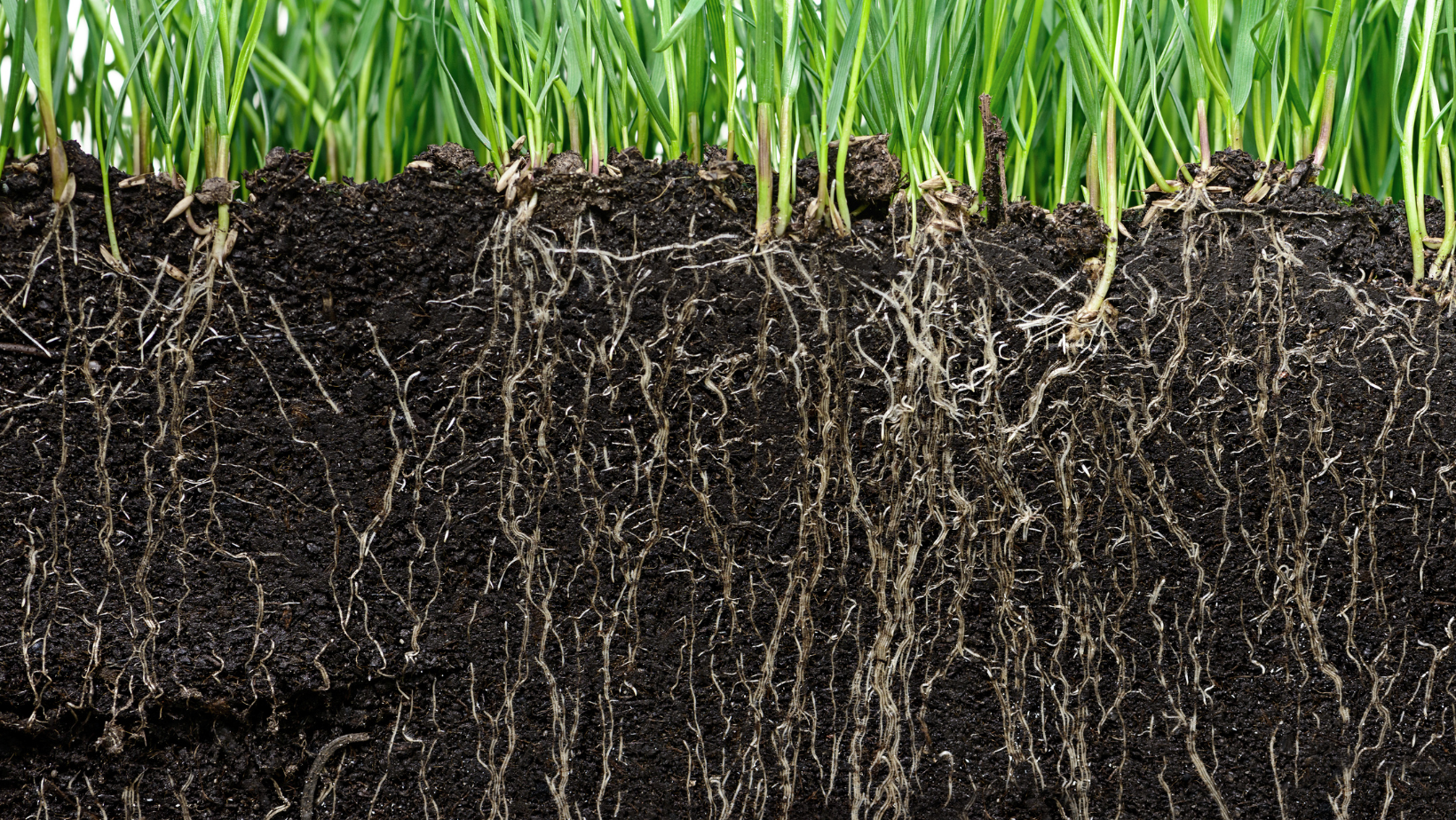
Soil Test
Read More: Soil TestA soil test involves the process of analyzing a sample of soil to determine its characteristics and quality. Scientists, farmers, turf caretakers, gardeners, and agricultural experts are all know to conduct soil testing. Assessing fertility, pH levels, nutrient content, and composition, are common reasons for conducting soil testing. Soil Testing Specifically, the benefits achieved by…
-
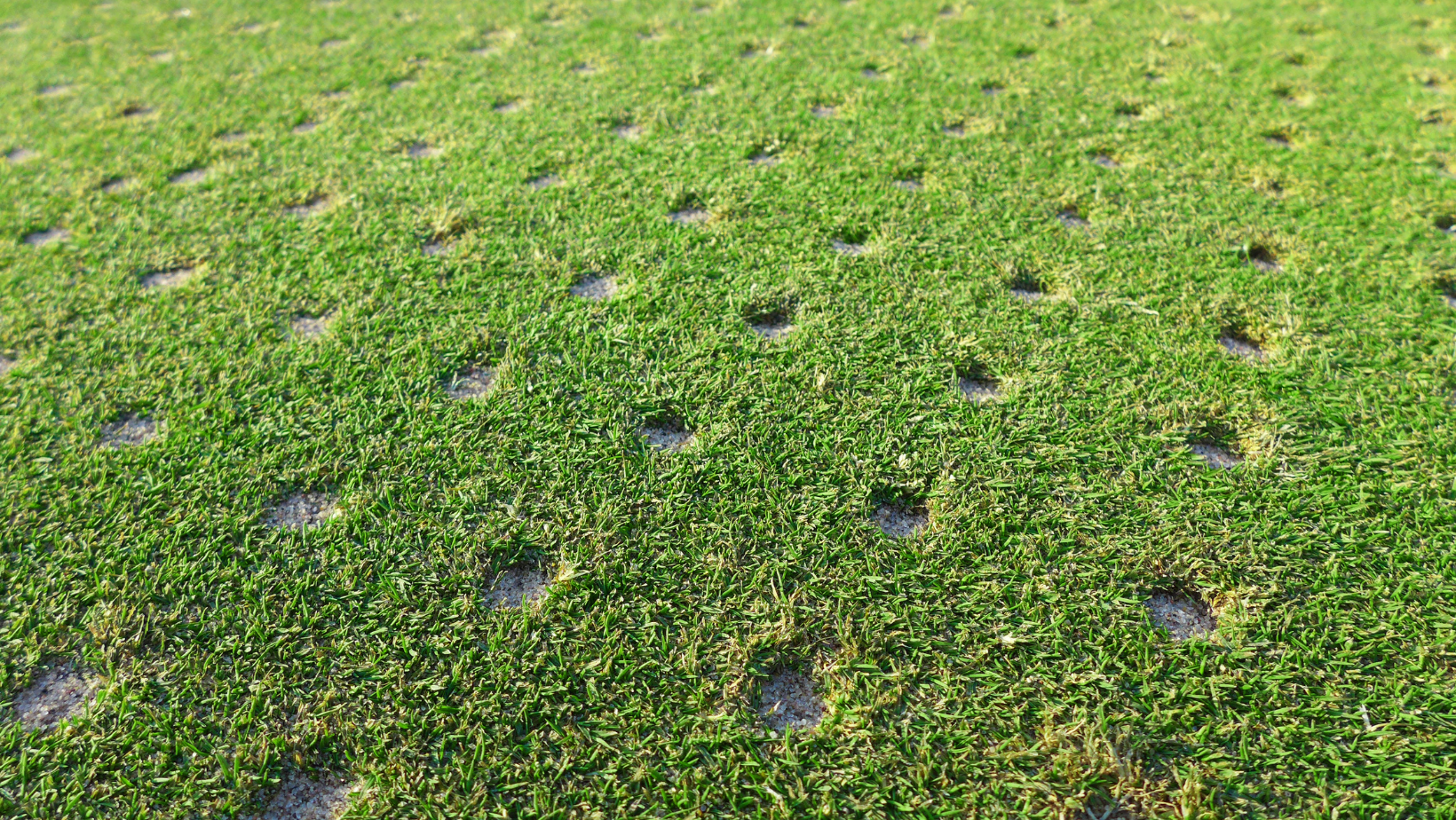

Aeration
Read More: AerationAeration is the process of introducing air or oxygen into a substance or environment. In the context of soil, aeration refers to the loosening or perforation of the soil to promote the exchange of air and water between the soil and its surroundings. Aeration enhances root growth, nutrient absorption, and soil structure in lawns, gardens,…
-

Bacteria Roles in the Carbon Cycle
Read More: Bacteria Roles in the Carbon CycleIndeed, bacteria play several important roles in the carbon cycle, which is the biogeochemical cycle that describes the flow of carbon between the atmosphere, land, and oceans. 1. Decomposition: Firstly, bacteria are primary decomposers in ecosystems. They break down dead organic matter, such as plants and animals, releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) back into the atmosphere.…
Search
Categories
Popular Posts
-
Redox Potential
Redox potential (Eh) and pH are two important factors that play significant roles in soil/plant/microorganism systems. They act as drivers, influencing various processes and interactions within these systems. This transdisciplinary overview aims to provide an integrated understanding of the relationships between redox potential, pH, and the functioning of soil/plant/microorganism systems. Thus, highlighting potential opportunities for…
-
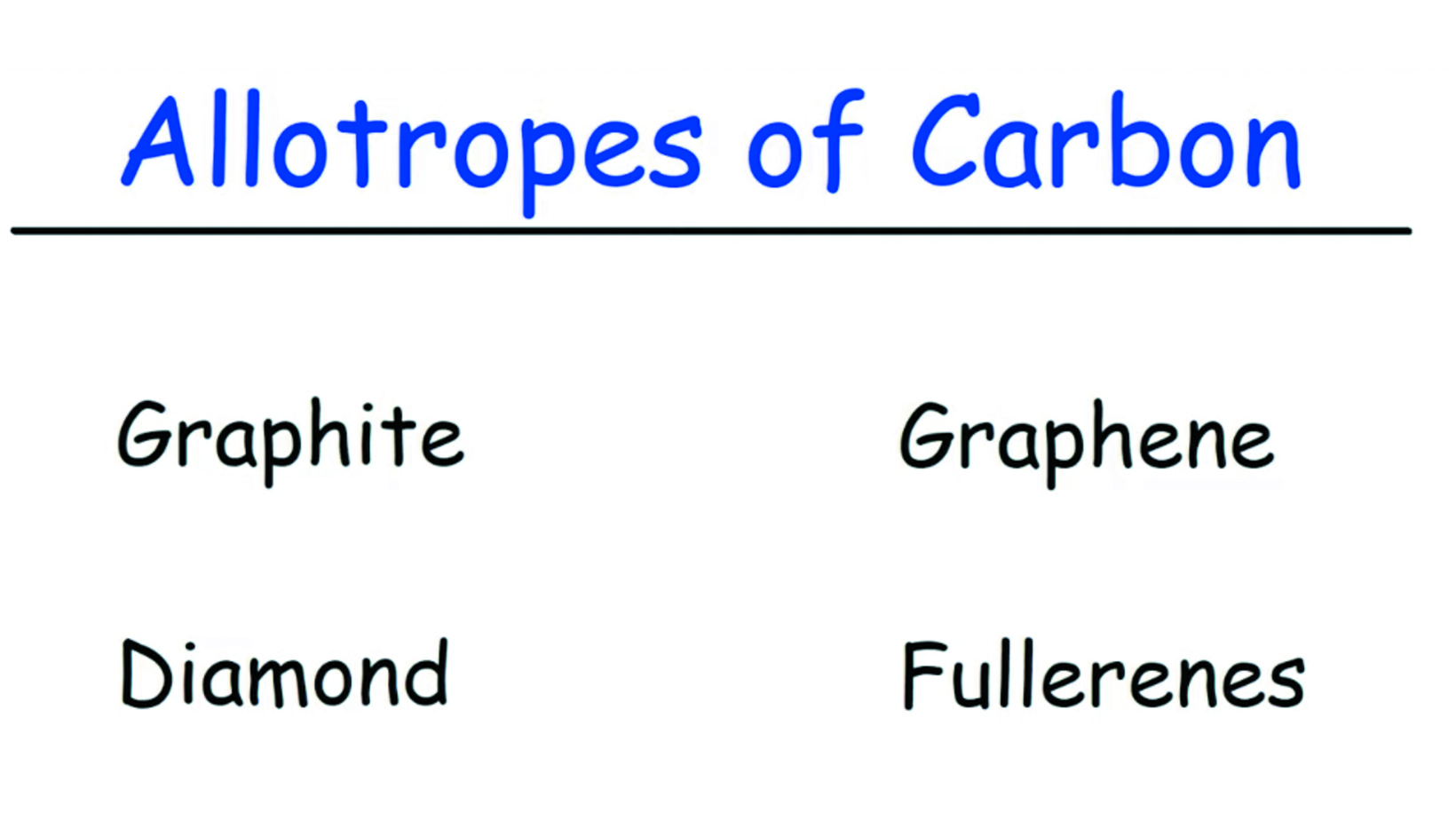
Allotropes of Carbon – Graphite, Diamond, and Graphene
We think that The Organic Chemistry Tutor summed this up rather nicely. Enjoy!
-
Graphite vs. Carbon
A Diamond Is Forever – Graphite vs. Carbon Graphite and diamond are both crystalline forms of pure carbon. The permanence of the carbon bonds separate them from all other forms of carbon. Well documented, soil carbon is extremely important. Soil metagenomics illusidates the carbon function. Specific application to nitrification and dentrification has been used to…