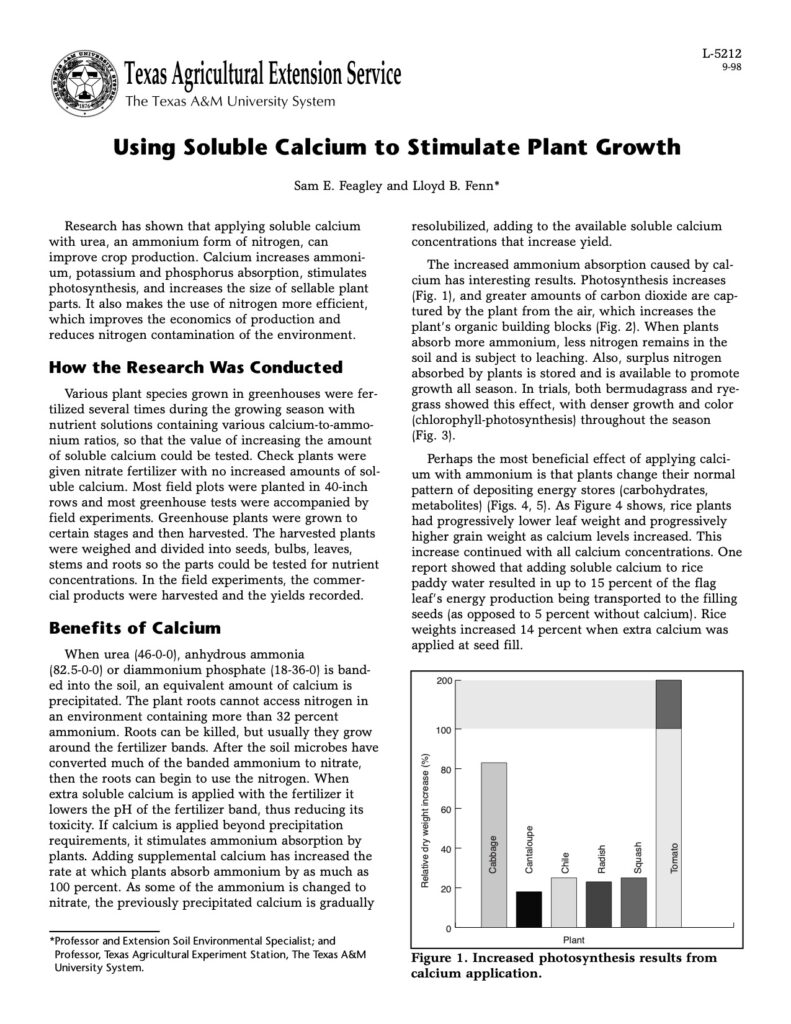
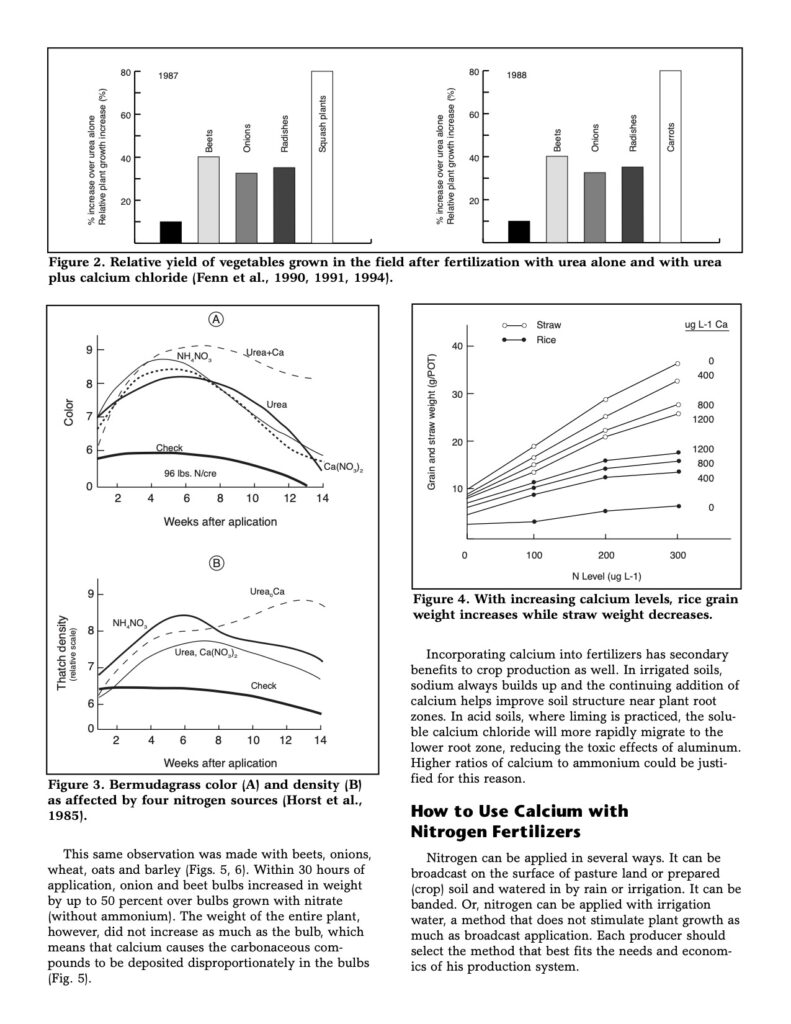
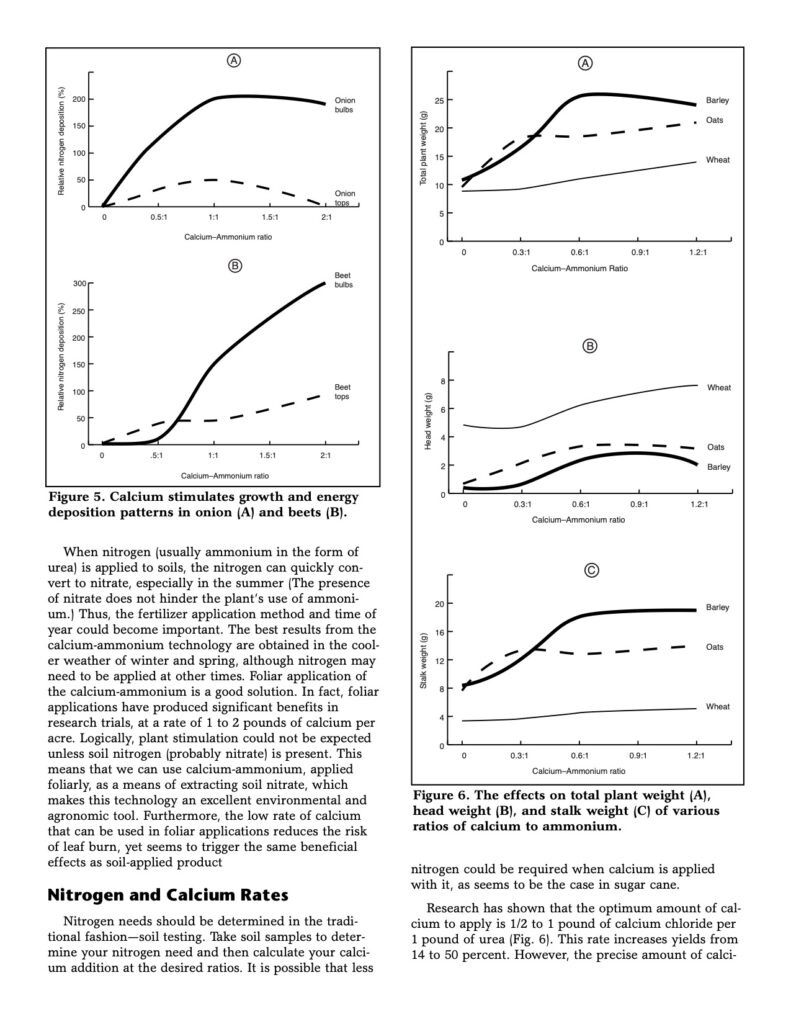
Soluble calcium is a vital nutrient for plant growth and development. It plays a crucial role in various physiological processes within plants, including cell division, enzyme activity, and nutrient uptake. When added to the soil or applied as a foliar spray (fertigation), soluble calcium can stimulate plant growth in several ways:
1. Root development: Soluble calcium enhances root growth and development by improving the stability and structure of cell walls in root tissues. This leads to stronger and healthier roots, allowing plants to absorb water and nutrients more efficiently.
2. Nutrient uptake: Calcium is necessary for the uptake and transportation of other essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus. It helps create a favorable soil environment for nutrient availability, promoting better nutrient absorption by plant roots.
3. Disease resistance: Adequate calcium levels in plants contribute to stronger cell walls, making plants more resistant to diseases and pests. It acts as a physical barrier against pathogens and reduces the risk of infection and damage.
4. Stress tolerance: It aids in plant adaptation to environmental stressors, including drought, heat, and cold. It enhances plant resilience by improving water and nutrient availability, as well as maintaining proper cellular functions under adverse conditions.
5. Fruit development: Calcium plays a vital role in fruit growth and quality. It helps prevent disorders like blossom-end rot in tomatoes and bitter pit in apples. Adequate calcium supply during fruit formation ensures better size, color, and texture.
Soluble Calcium and Fertigation
To effectively stimulate plant growth using soluble calcium, it is important to apply the nutrient at the right time and in the correct form. It can be applied through fertilizers, such as calcium nitrate or calcium chloride, or as a foliar spray. The application rates and timing may vary depending on the specific plant species and growing conditions. Fertigation is the perfect vehicle for meeting these requirements.
We recommend conducting a soil test to determine the current calcium levels and to understand the specific needs of the plants being cultivated. This will help in making informed decisions regarding the appropriate calcium fertilizer and application method. Additionally, testing will determine if consideration other nutrient requirements is necessary to optimize plant growth and health.
Texas A&M’s Agricultural Extension Service research provides much deeper insight on this nutrient.